What is gelatin? Should I replenish gelatin? Nutritionists remind you that it is more effective to eat together with "1 item"

Collagen is the highest protein in the human body, accounting for more than 25% of the total protein in the body, and is widely distributed in all parts of the body, such as the skin, soft bones, straps, tendons, cornea, blood vessel walls and internal organs, which have its traces.
- composition and structure of gelatin proteinIt is a fiber-containing glycoprotein, which is basically a triple helix protein molecule composed of 3 polypeptide chains. Each polypeptide chain contains about 1,000 amino acids. The main amino acids in it are glycine, proline, hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine. These gelatin molecules will then be connected into a larger structure to exert its function.
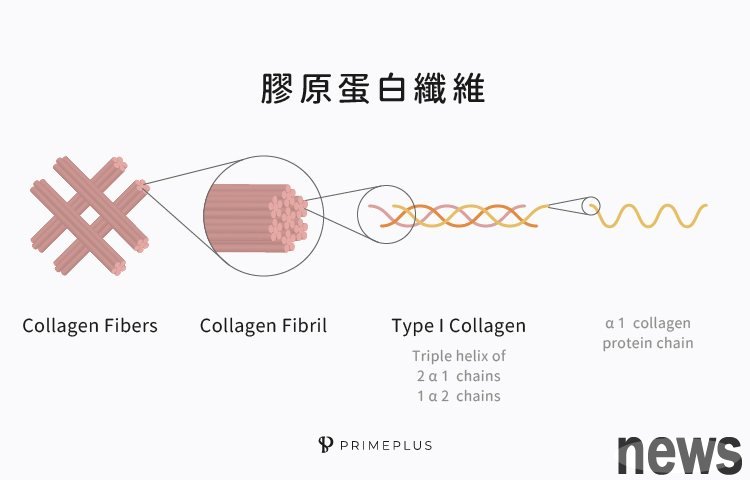
The gelatin proteins that have been discovered are at least 28 types, and different types of gelatin proteins will also be different in structure and function. Among them, the first type and the second type are more often discussed. Type 1 gelatin is the type with the most content in the body and is also the main gelatin in the skin. Type 2 gelatin is commonly seen in soft bones.
Phyalmic functionDifferent types of gelatin proteins can provide different physiological functions, allowing us to describe several examples:
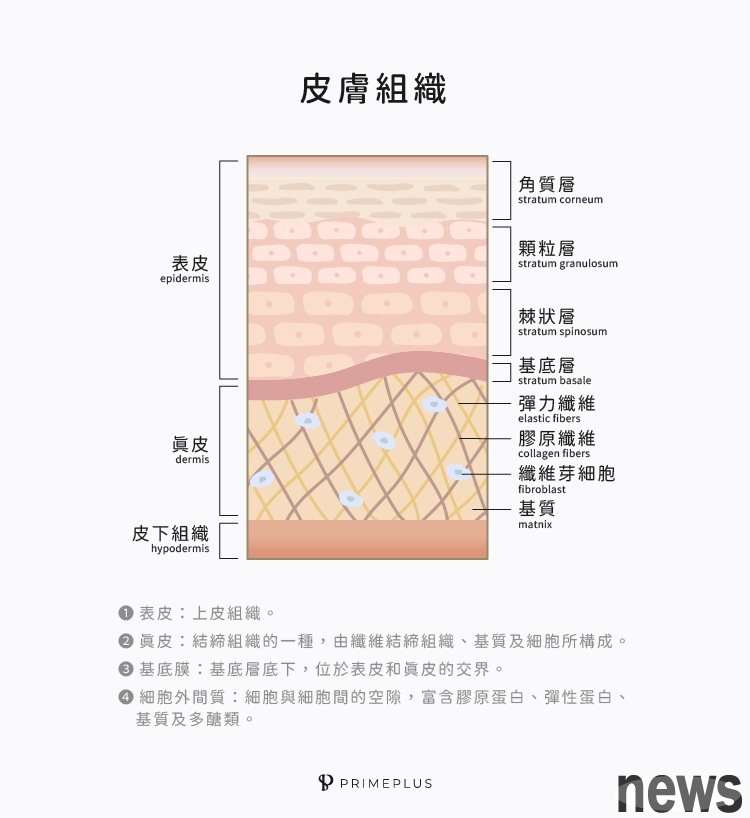
It is an important component of cell quality. The cell quality is the void between cells and cells, divided into two parts: Fiber wiki and fluid matrix. Glycogen is a member of Fiber wiki. It can be used as a cell adhesion protein, connecting cells, and also provides structural and support functions. The skin can support skin cells to prevent the surface from collapsing, and can also maintain skin elasticity with elastic fibers.
is mainly present in the junction structure and has the functions of supporting and protecting internal organs. There is a structure called the basement membrane in the organ, which is part of the cervical tissue, usually located on the cavity or the surface of the organ (on the next layer of the epithelial tissue). This structure can be used to fix the epithelial tissue on the cervical tissue, or it can be used as a mechanical barrier to protect the organs, and gelatin is one of the components of the basement membrane.
Skin tissue layer
 The mechanical properties of the
The mechanical properties of the
gelatin fibers can provide the tension and strength required for the organization, and resist external pressures. These characteristics make Korean belts and tendons less likely to break when stretched, making the blood vessel wall elastic and helping the soft bone withstand body pressure.
has the function of assisting wound combinatorial and organizational repair, and assisting coagulation and other functions.
can perform functions of regulating cell growth, differentiation and migration through the receptor.
Complementation of gelatinFrom the above content, we have a general understanding of the functions and roles of gelatin in the human body. However, as the age increases, due to external destruction factors and internal creators, the gelatin protein is gradually lost due to the synthesis trend, the rate of molecules being broken and decomposed increases, and then it affects some physiological functions and reacts to the appearance. Therefore, in order to retain more gelatin protein in the body, some people will wonder whether to use gelatin supplements? Before answering this question, we can discuss the synthesis of gelatin.
Protein is composed of many amino acids, and amino acids are divided into essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids. Among them, the essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the human body and need to be continuously supplemented through diet to meet the needs of the body. Non-essential amino acids are amino acids that can be synthesized by the human body. The three main amino acids that form gelatin (glycinic acid, proline and lysine) are all non-essential amino acids, which means that if you can eat a balanced diet and maintain a good living habit, you may get enough raw materials to synthesize gelatin!
Then why should gelatin be supplemented? It is to directly provide the raw materials needed for the body to synthesize gelatin and improve the chance of synthesis! The gelatin protein eaten through diet is actually not directly transformed into the gelatin protein in our body. It will be decomposed from the digestive tract first, and then absorbed into the body in the form of small molecule peptides (dipeptides, tripeptides, etc.) or amino acids. Then these molecules will circulate to the body, which may synthesize gelatin proteins (synthesised by vitiligo cells) in the skin or soft bones, or may be repaired in various parts of the body, or as raw materials for synthesis of other substances. Among them, the small molecule dipeptide of gelatin protein Pro-Hyp (PO) has the effect of stimulating the appearance of vitiligo cells and can promote hyaluronic acid synthesis. Therefore, eating gelatin protein not only provides sufficient synthetic raw materials for the body, but also stimulates the appearance of virgin cells. At this time, the "gelin molecular size" that comes in is a major point.
In addition to replenishing gelatin, through some adjustments to life and dietary habits, it can also reduce the loss of gelatin, such as: daily routines to improve the new cervical dysfunction, prevent and reduce UV radiation, etc.; in diet, foods containing antioxidants can be selected (such as cetathione, vitamin C, vitamin E and β-Hussarin, etc.) to protect gelatin from being damaged. Among them, vitamin C also has the function of promoting the synthesis of gelatin protein.
Core of synthesis of gelatin – Vitamin CViocin C participates in the key step of synthesis of gelatin. It is an important enzyme for regulating oligosine into oligosine reaction. If the internal vitamin C is not sufficient and the reaction is reduced, it will affect the synthesis of gelatin. Therefore, it is particularly important to hope that the gelatin can be produced smoothly!
Even if the human body can synthesize gelatin by itself, it will be affected by age, body quality and environment, which will lead to the rate of gelatin gain through general diet, which may not be as good as the rate of loss. Therefore, direct replenishing gelatin is also one of the options. However, considering various factors such as personal quality and supplemented gelatin quality, the effect produced varies from person to person. Therefore, whether to supplement gelatin additionally can be carefully evaluated according to personal needs.




