When you are old, you need to do muscle strength training. Lighter resistance can also increase bone density and reduce chronic disease risks.

Muscle strength training is a series of resistance movements for different muscle groups, helping to improve strength and muscle endurance. For older people, benefits of muscle training include: enhancing independent autonomy, improving balance and mobility, increasing bone density and reducing chronic disease risks. However, many myths have made the older person miss this kind of squirting and a richer life.
Myth 1: The elderly cannot strengthen their muscle strengthError! Many studies (including a study by Professor Brigham and Women 's Hospital Kieran Reid and his team at one of the Harvard Medical College Teaching Hospitals in the United States) have shown that seniors who continue to perform muscle strength training have significantly improved their sense of movement, strength and balance.
They compared light and heavy training plans, and found that both can effectively improve muscle strength and explosiveness. Regardless of age or health at that time, older people can still become stronger, increase muscle mass, and improve body function, even if they do lighter resistance exercises.
Myth 2: Muscle strength training is dangerous and easy to get hurt for older people.On the contrary, strength training can protect the correlation and reduce inflammation, which can help reduce the risk of injury. By increasing muscle strength and stability, it can reduce stress. In addition, strength training can also stimulate the release of anti-inflammatory substances (cytohormones) in the body, helping to reduce inflammation and prevent sports injuries. As long as there is correct guidance and appropriate strength, muscle strength training is very safe and effective.
Myth 3: It is safe for a long person to only make a light weightslightly heavier weight, the key is to understand its own limitations. Muscle strength training requires a process of gradually increasing strength. Start with light, and wait until you feel appropriate and have more confidence in your abilities, and then slowly increase resistance. Focus on maintaining correct posture, and pay attention to signals such as inappropriate muscles or fatigue caused by your body.
Myth 4: Seniors need to go to the gym or use professional equipment to do muscle training.Many household items such as soup cans, laundry baskets, and large-capacity plastic containers with handles can be used for simple and refined training. In addition, bare hands training such as squats, lunges, and erecting on the ground can be adjusted based on personal muscle strength.
Find the movement methods you like and devote to, set real goals, and record progress, so that muscle strength training becomes fun and full of accomplishment! Strengthen your muscles and allow you to handle daily life tasks more easily: lift heavy objects, push your waist and lift things, do some garden activities, and up and down stairs.
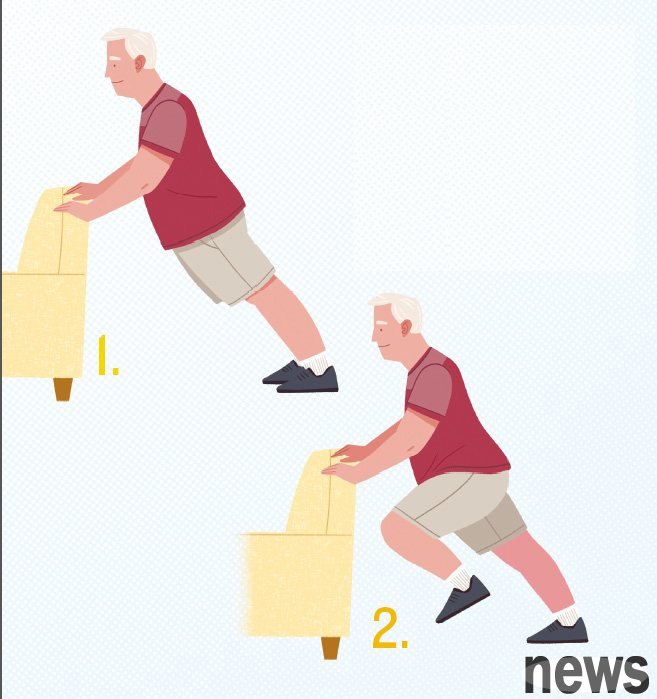
Pinning muscle group: abdominal muscles, calf muscles, deltoid muscles, gluteal muscles, back leg muscles, trine muscle climbers are one of my favorite moves, which not only improves speed and balance, but also improves reaction time to avoid falling. Improved reaction time is to speed up the speed you can move your legs, helping you regain balance. This exercise can train multiple muscle groups, and hiking will no longer be a headache!
Action instructions
1. Stand position preparation: place both hands on the kitchen wall or the backrest of the sofa, positioned directly under the shoulders, and both hands are the same width as the shoulders. Take a step back and let the body look slightly toward the edge or the front of the sand. The back should be kept straight, ensuring the straight line from head to foot.
2. Alternate knee lifting action: step on the ground with your right foot and lift your left knee toward your chest. No need to stop, change your legs later, put your left foot back on the ground and step on your sturdy posture, then raise your right knee and lean towards your chest. At the speed you can do, keep alternating the two-leg movements smoothly and vigorously as much as possible, and keep the core stable and powerful. The back remains in a straight line from head to foot.
3. Number of training sessions: 8 to 12 times are completed, 2 to 3 groups are carried out in total, and the groups are rested for 30 to 60 seconds.
Reduce the difficulty: You can start slowly and focus on making the posture correct. You can also do this with a higher table or a tilt to reduce the burden on your arms and shoulders.
Improve difficulty: Change to doing it on the ground, use a stance to stand up, and increase the number of times and speed. You can also add a stumbling step after each leg lift.
Reminder: Focus on your breathing, take a deep breath when you put your knees toward your chest; exhale hard when you put your knees down. When you start to feel tired, keep your body in a straight line and do not push your waist forward.
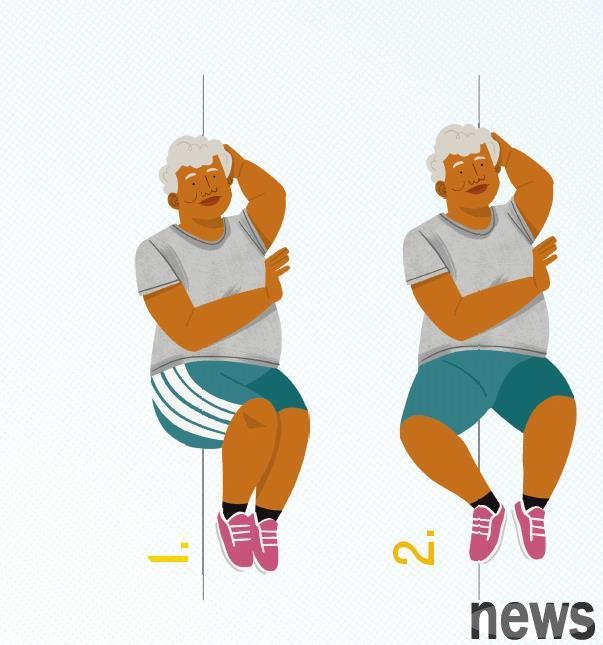
Panther muscle group: Glute muscles
age increases, and the muscles in the lateral area are prone to weakening and weakening. Inability to the lateral part will lead to poor balance and difficult walking, which will increase the risk of falling. The clam combo is a simple but very effective exercise that strengthens the muscles of the body and helps the pelvic stability as you walk and climb the stairs.
Action instructions
1. Preparation posture: Lying on the left side, with the left arm supporting the head. Put your legs together and gently bend your knees. Place your right hand on the front floor to help stabilize your body.
2. Opening action: Keep your feet tied up and raise your knees as much as you feel comfortable, like a shell opens. Stay at the highest point above for 1 to 3 seconds before returning to the starting position.
3. Number of training sessions: 8 to 12 times per side is 1 set. Make 2 to 3 sets on each side, and the sets are rested for 30 to 60 seconds.
Reduce difficulty: Do not lift the legs too high and reduce the range of movement. Clutch a pillow between the knees to make the upper leg more easily lifted.
Improve difficulty: Use resistance straps on the thighs, i.e. above the knee, and slow down during movement, extending the tightening time of the lateral muscles. Or increase the number of times per group.
Reminder: Retract the core and do not let the pelvis tilt backward during the operation. Make sure that the action starts from the hair and the lower back does not move. When you lift your legs, you should be able to feel the contraction of your hips and hair muscles.





