I am reluctant to sterilize my dog. What should I do if my scrotum gets inflamed?
Whenever the skin in the rich parts of the scrotum, perineum and other parts of the sweat glands have eczema-like changes, you should think of the possibility of scrotitis in dogs and cats. Although it is not very harmful, it is very troublesome. In the early stage, there are small blister-like rash or scaly erythema, with clear boundaries, and surface erosion, seepage, and scab after scratching. After the scabs fall off, the skin becomes warty-like hyperplasia and gradually infiltrates outward, forming rough skin lesions that intersect erosion and erythema, which often has a disgusting odor due to secondary infection.
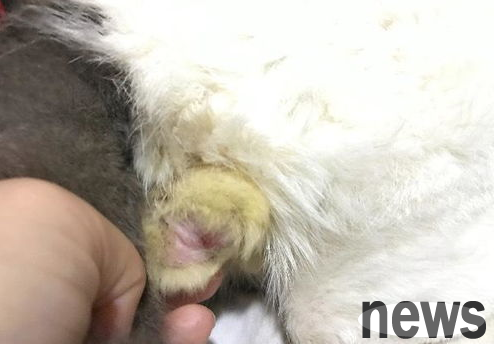
scrotitis usually has three types:
1. The erythema type is symmetrically distributed on the two sides of the scrotum, about 3×4cm in size, with bright erythema on the edges, covered with gray or brown thin scabs, and the surface is rough. After stripping off the scab, the slightly reddish skin was exposed without significant moisture. The damage can be fused at the root of the penis when it expands.
2. The papule type begins to have several scattered soybean-sized papules on one side of the scrotum, which are significantly higher than the skin, flat, covered with thin brown scrots, and later it increases and expands, and is densely symmetrically distributed on both sides of the scrotum suture, about 3×4cm, fuses into pieces, and is often fused at the root of the scrotum. There is irregularity in the coronal groove of the penis, which is significantly higher than the thick gray-black scabs on the skin, and gray scales on the penis. There are sporadic folliculitis or abscesses in the pubic bone and groin.
3. White papules. Psoriasis type. This type is rare, but it is very typical. A large piece of the scrotum is fused by a flat papule the size of melon seeds, with silvery white, and when caught, silvery white scales fall off.
Brief description of 5 symptoms of scrotitis
1. Scrotum dermatitis: The cause may be related to the lack of B vitamins in the diet. The symptoms are flushing, oozing, peeling, and even blisters, which are painful and itchy.
2. Scrotal eczema: mainly caused by sweat and filth stimulation. It is manifested as redness, swelling, blisters, oozing, scabs, and even thickening and rough, which is unbearable.
3. Scrotal tinea: A skin disease caused by mold infection, which is often related to tinea tinea in other parts of the patient. The skin of the scrotum is flushed, papules or blisters, and then dandruff. The lesion site is often damaged in an annular shape and it is severely itchy.
4. Riboflavin deficiency scrotitis: It is more common in men who eat sperm white rice, sperm white flour all year round, or long-term diarrhea, constipation, loss of appetite or picky food. The main manifestations are: the scrotum is slightly red and shiny at the beginning, and then light red spots appear on both sides of the scrotum, with scales stuck on it. Soon, multiple flat papules the size of soybeans will appear, with varying degrees of itching, often accompanied by angular stomatitis and glossitis.

5. Scrotal simple collar: that is, neurodermatitis in the scrotal area. Its characteristics are that the skin is itchy, thickened and thickened, but it is impermeable to liquid, and the course of the disease is often long and difficult to heal repeatedly.
How to prevent and treat:
1. The weather is hot and the temperature is rising. Try not to walk the dog in the bushes or grass, as it can easily stimulate the sensitive scrotum. .
2. Non-sterilized estrus or unhealthy mating is another major cause of scrotitis.
3. Apply topically anti-inflammatory, antifungal or low-concentration glucocorticoid cream to supplement vitamins.
4. Pay attention to cleaning and hygiene and keep it dry.
5. Be careful to wear Elizabeth's circle, otherwise no matter how good the treatment is, it will be useless.
6. When local damage is serious, you should go to the hospital for diagnosis and treatment as soon as possible.




